Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Qingdao University, Qingdao 266071, People’s Republic of China
2 Optics and Thermal Radiation Research Center, Institute of Frontier and Interdisciplinary Science, Shandong University, Qingdao 266237, People’s Republic of China
3 School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shandong University, Jinan 250100, People’s Republic of China
4 Ultrafast Optics and Nanophotonics Laboratory, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB T6G 2V4, Canada
Vanadates are a class of the most promising electrochromic materials for displays as their multicolor characteristics. However, the slow switching times and vanadate dissolution issues of recently reported vanadates significantly hinder their diverse practical applications. Herein, novel strategies are developed to design electrochemically stable vanadates having rapid switching times. We show that the interlayer spacing is greatly broadened by introducing sodium and lanthanum ions into V3O8 interlayers, which facilitates the transportation of cations and enhances the electrochemical kinetics. In addition, a hybrid Zn2+/Na+ electrolyte is designed to inhibit vanadate dissolution while significantly accelerating electrochemical kinetics. As a result, our electrochromic displays yield the most rapid switching times in comparison with any reported Zn-vanadate electrochromic displays. It is envisioned that stable vanadate-based electrochromic displays having video speed switching are appearing on the near horizon.
Nano-Micro Letters
2023, 15(1): 229
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 China Academy of Space Technology (Xi’an), Xi’an 710110, China
2 School of Electronic Information, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710129, China
3 The Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology & Systems (Ministry of Education), Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
4 Artificial Intelligence Center, Peng Cheng Laboratory, Shenzhen 518000, China
Frequency-swept interferometry (FSI) is a well-known ranging technique, but it suffers from three problems, namely, the Doppler effect, the frequency-sweep nonlinearity, as well as the slow frequency-sweep rate. The first two problems hinder the measurement accuracy, while the third problem limits the measurement rate. In this paper, we present a dynamic FSI (DFSI) that solves these three fundamental problems simultaneously. The DFSI consists of two auxiliary interferometers (AU1 and AU2) and two measurement interferometers (FSI and frequency-fixed interferometry (FFI)). We use FSI to obtain the Doppler and nonlinearity affected ranging signal, AU1 to monitor the frequency-tuning nonlinearity in the frequency-swept laser (FSL), and FFI and AU2 to constitute a laser vibrometer for monitoring the target motion-induced Doppler effect. Then, a novel signal fusion processing technique is applied to reconstruct the real dynamic distance from the above-measured signals. The dynamic ranging error caused by the Doppler effect and frequency-sweep nonlinearity in FSI can be eliminated and the dynamic distance at each sampling point can be obtained. The validity of this method is demonstrated by numerical experiments.
光电子快报(英文版)
2022, 18(11): 662
1 内蒙金属材料研究所,包头 014000
2 华中科技大学材料科学与工程学院,武汉 430073
3 山东大学晶体材料国家重点实验室,济南 250100
采用全反模式的红外(ATR-IR)光谱实时研究了不同氘含量KH2-xDxPO4(DKDP)晶体的结晶过程,其中DKDP溶液氘含量范围为0到99%。通过υ1(PO4)和υ3(PO4)振动表征了DKDP结晶溶液中(H2PO4-)1-x(D2PO4-)x离子基团浓度的变化。υ1(PO4)振动强度的变化和υ3(PO4)振动宽度的变化说明生长溶液中的(H2PO4-)1-x(D2PO4-)x离子浓度随着测试时间延长而不断增大。同时,δ(P-O…H/D-O-P)振动峰的形成说明DKDP晶体的生长基元为(H2PO4-)n-x(D2PO4-)x离子团簇。波数在1 448 cm-1到1 653 cm-1范围内H-O-H和D-O-D振动强度的变化解释了DKDP晶体在结晶过程中氘含量分布不均的现象。
DKDP单晶 结晶过程 ATR-IR光谱 (H2PO4-)n-x(D2PO4-)x团簇 氘含量 生长基元 DKDP single crystal crystallization process ATR-IR spectroscopy (H2PO4-)n-x(D2PO4-)x clusters deuterium content growth unite
1 中国空间技术研究院西安分院空间微波技术国家级重点实验室, 陕西 西安 710100
2 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所空间激光传输与探测技术重点实验室, 上海 201800
3 北京跟踪与通信技术研究所, 北京 100094
对多相移光纤光栅滤波器的光谱进行了理论仿真。理论结果证明:通过精确设计多相移光纤光栅的相移点数目、相移位置分布、耦合系数、长度等参数,可以获得窄带平顶滤波响应的光谱;而实际制备中引入的误差会导致滤波器光谱性能恶化。随后采用紫外辐照后处理的方式,制备了多相移光纤光栅滤波器,并对其光谱进行了测试。结果表明:当多相移光纤光栅滤波器带宽较宽时,实测光谱与理想仿真结果较为吻合;增大耦合系数以减小带宽时,滤波器的性能对工艺误差更敏感。最后对误差项进行了深入的分析与讨论,结果证明,采用较长的多相移光纤光栅可以有效地增大相移点位置和相移差的容限,减弱光致损耗对其性能的影响。
光纤光学 多相移光纤光栅 紫外辐照后处理 微波光子信号处理 光学学报
2020, 40(22): 2206002
1 暨南大学材料科学与工程系, 广东 广州 510632
2 暨南大学附属第一医院, 广东 广州 510632
聚赖氨酸是一种重要的聚阳离子, 在生物医药领域具有广泛的应用前景。 但是, 目前其血液相容性的相关报道较少, 特别是通过光谱法研究其与血液中重要蛋白的相互作用。 因此, 通过多种光谱法研究聚赖氨酸与纤维蛋白原的相互作用, 进一步评价其血液相容性具有一定的创新性。 本实验通过荧光、 紫外和圆二色谱研究聚赖氨酸对纤维蛋白原结构的影响。 其中, 聚赖氨酸的正电性随着浓度增大而增大; 复合实验显示, 0.01 mg·mL-1的聚赖氨酸对纤维蛋白原的功能影响较小, 随着浓度增大, 相互作用增强; 荧光光谱显示, 纤维蛋白原在λem=341 nm处出现浓度依赖性的荧光猝灭; 紫外光谱显示, 聚赖氨酸对纤维蛋白原吸收强度(200~240和278 nm处)的影响在0.025 mg·mL-1时较小, 并出现浓度依赖性的减少; 圆二色光谱显示, 随着聚赖氨酸浓度增大, 纤维蛋白原的α-螺旋含量减少, β-折叠、 β-转角和无规卷曲含量增加。 结果表明, 聚赖氨酸会与纤维蛋白原发生静电相互作用, 对其结构造成浓度依赖性的影响。 当浓度为0.01和0.025 mg·mL-1时, 聚赖氨酸对纤维蛋白原结构的影响较小; 而浓度过大时, 影响较大, 势必破坏纤维蛋白原的生理功能。 因此, 研发和应用聚赖氨酸时必须充分考虑浓度因素。 本实验提供了一种简便而系统的方法来研究材料与蛋白的作用,有利于充分评价材料的血液相容性。 此外, 上述研究结果对聚赖氨酸的生物医学应用具有重要的指导意义。
聚赖氨酸 纤维蛋白原 荧光光谱 紫外光谱 圆二色谱 Poly-L-lysine (PLL) Fibrinogen Fluorescence spectroscopy UV Circular dichroism
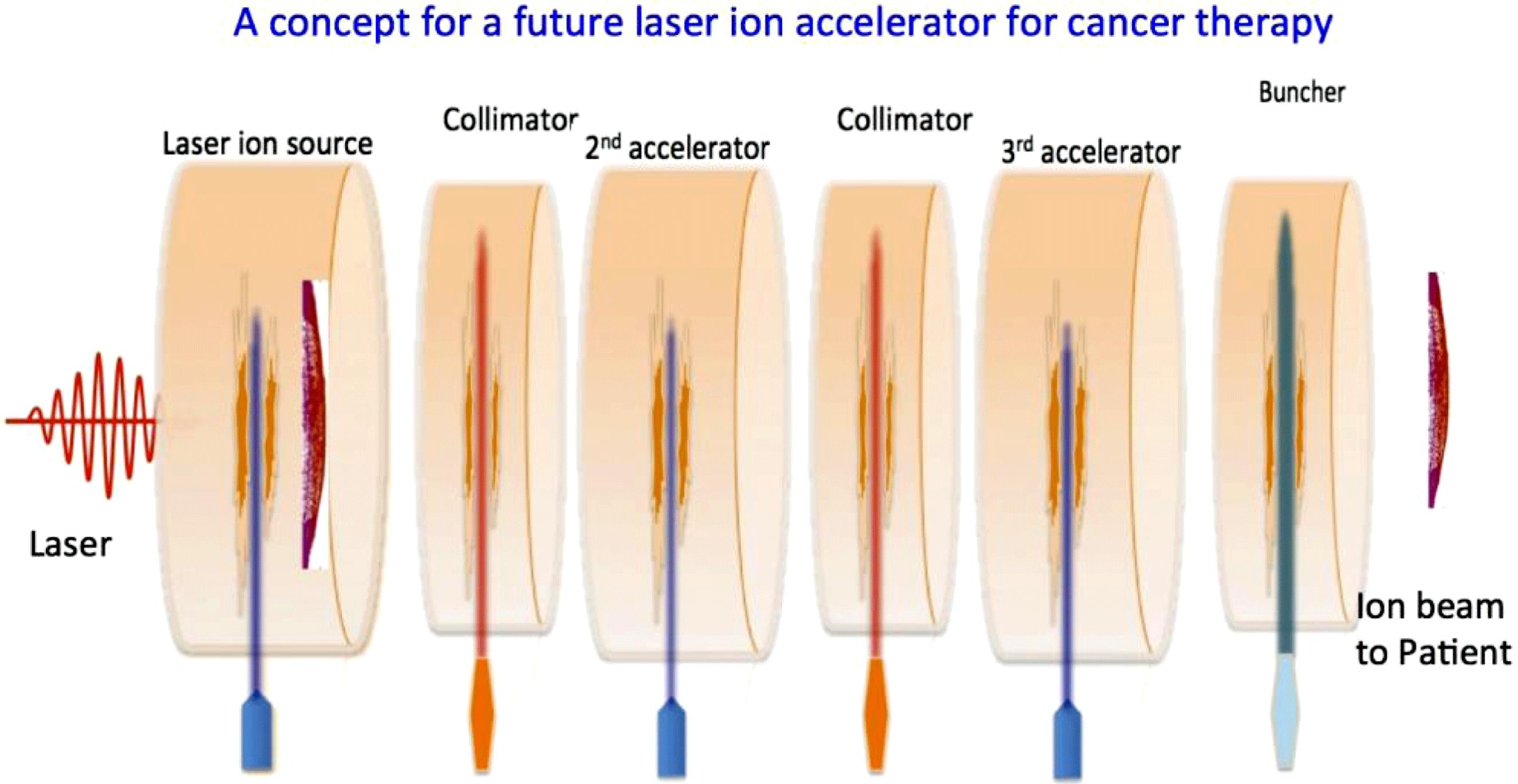
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Advanced Interdisciplinary Sciences, Utsunomiya University, Yohtoh 7-1-2, Utsunomiya 321-8585, Japan
2 CORE (Center for Optical Research and Education), Utsunomiya University, Yohtoh 7-1-2, Utsunomiya 321-8585, Japan
3 School of Computer Engineering and Sciences, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China
4 Institute of Modern Physics, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
5 Department of Physics, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
6 Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100080, China
An ion beam has the unique feature of being able to deposit its main energy inside a human body to kill cancer cells or inside material. However, conventional ion accelerators tend to be huge in size and cost. In this paper, a future intenselaser ion accelerator is discussed to make the laser-based ion accelerator compact and controllable. The issues in the laser ion accelerator include the energy efficiency from the laser to the ions, the ion beam collimation, the ion energy spectrum control, the ion beam bunching, and the ion particle energy control. In the study, each component is designed to control the ion beam quality by particle simulations. The energy efficiency from the laser to ions is improved by using a solid target with a fine sub-wavelength structure or a near-critical-density gas plasma. The ion beam collimation is performed by holes behind the solid target or a multi-layered solid target. The control of the ion energy spectrum and the ion particle energy, and the ion beam bunching are successfully realized by a multi-stage laser–target interaction.
Intense short-pulse laser laser ion acceleration laser ion cancer therapy laser–plasma interaction High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2014, 2(1): 010000e4
1 安徽工业大学材料科学与工程学院, 安徽 马鞍山 243002
2 马钢技术中心, 安徽 马鞍山 243000
用Nd:YAG固体脉冲激光焊接器对厚度为0.65 mm的DP500双相钢进行了激光焊接试验,对脉冲激光焊缝表面和横截面形貌进行了分析,重点研究了不同脉冲激光频率下焊缝凝固特征及晶粒组织与硬度的关系。试验结果表明,在形成焊缝的每个焊斑可分为重叠区和未重叠区,并且随着脉冲激光频率不同,不但形成的焊缝形态和焊斑重叠率不同,而且还存在晶粒组织的差异。同时,硬度出现波动性,最低硬度值出现在焊斑重叠区,最高硬度值出现在焊斑未重叠区。随着脉冲激光频率的提高和焊斑重叠率的增大,晶粒组织的差别不但逐渐减小,而且沿焊缝正剖面中心线的硬度波动性也逐渐降低。
激光技术 脉冲激光焊接 焊缝凝固特征 显微组织 双相钢 显微硬度
兰州大学大气科学学院, 半干旱气候变化教育部重点实验室,甘肃 兰州 730000
为了研究中国西北半干旱区卷云几何特征和光学特性的时空分布特征, 利用兰州大学半干旱气候与环境观 测站(SACOL, 35�57�N, 104�8�E) 的微脉冲激光雷达(MPL-4B)探测卷云过程,分析讨论了卷云的结构、 光学性质及其时间变化特征,结果表明,卷云高度分布范围为 7~10 km, 卷云经历了薄-厚-薄的过程, 平均厚度为 (2.0±0.5) km。卷云环境温度在 -51℃-39℃范围之内。卷云的光学厚度在 0.084~1.649 之间, 光学厚度随几何厚度的增加而增大,平均光学厚度为 0.651±0.403。卷云激光雷达比为 (17±17) sr。 薄卷云的激光雷达比要比厚卷云的大。光学厚度小于0.3的光学薄卷云出现高度在8.6 km以上, 环境温度低于-45℃, 几何厚度小于1.8 km, 雷达比分布在5~69 sr。
遥感 几何和光学特征 透过率法 卷云 remote sensing geometrical and optical properties transmittance method cirrus clouds
兰州大学大气科学学院, 半干旱气候变化教育部重点实验室,甘肃 兰州 730000
基于Fernald方法和Klett方法,推导出一个具有明确物理意义的 确定气溶胶消光系数边界值的表达式, 该式比目前用于确定边界值的Collis斜率法表达式增加了两项:空气分子消光系数项和后向散射项, 这两项与Collis斜率法的值符号相反。空气分子消光系数项较小,但后向散射项为后向散射系数的 倒数和导数的乘积,绝对值能达到Collis斜率法的75.2%。分析表明,考虑了新增两项反演的大气 气溶胶光学厚度(AOD)与实测更接近,所以增加这两项是合理的、必要的。不同标高反演2007年 9月20日的AOD在0.20~0.25之间,变化范围较小;反演的AOD方差为0.003, 相对较小。说明新方法对 标高的依赖较小且较稳定。分析424个时次晴空资料的反演结果可知,反演比实测大7.4%, 反演与实测的相关系数为93.2%, 相对误差和绝对误差分别为10.9%和0.03, 反演的AOD方差为0.02, AOD小于0.45(占到资料总数的91.7%)时,反演结果较好。
大气遥感 激光雷达 消光系数 边界值 标定高度 光学厚度 remote sensing lidar extinction coefficient boundary value reference height aerosol optical depth
马鞍山钢铁股份有限公司 技术中心,马鞍山 243000
为了研究汽车用高强钢中合金元素磷对激光焊接头质量的影响,采用12kW的CO2激光器对4.8mm厚的含磷高强度无间隙原子钢M250P1进行了高功率焊接。对不同焊接工艺参量下的焊接接头进行了成型试验、拉伸力学性能、显微组织和扫描电子显微镜能谱分析。结果表明,在特定焊接工艺参量下,M250P1焊接接头虽具有良好的拉伸力学性能和成型性能,但在形变过程中焊接接头仍容易在熔核区发生开裂,其主要原因是熔核区内金属在快速冷却时,磷元素来不及扩散,在晶界聚集,形成磷偏析,导致焊接接头韧性下降。
激光技术 磷偏析 焊接 含磷高强IF钢 laser technique phosphorous micro segregation weld P-added high strength interstitial free steel





